《J. Am. Soc. Chem.》: Regulated Photocatalytic CO2-to-CH3OH Pathway by Synergetic Dual Active Sites of Interlayer
Jiacong Wu,+ Fei Huang,+ Qinyuan Hu,+ Dongpo He, Wenxiu Liu, Xiaodong Li*, Wensheng Yan, Jun Hu, Junfa Zhu, Shan Zhu, Qingxia Chen*, Xingchen Jiao*, and Yi Xie*
Herein, composites of nanosheets with van der Waals contact are employed to disclose how the interlayer-microenvironment effects the product selectivity of carbon dioxide (CO2) photoreduction. The concept of composites of nanosheets with dual active sites is introduced to manipulate the bonding configuration and promote the thermodynamic formation of methanol (CH3OH). As a prototype, the CoNi2S4-In2O3 composites of nanosheets are prepared, in which high resolution transmission electron microscopy imaging, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy spectra, and Zeta potential tests confirm the presence of van der Waals contacts rather than chemical bonding between the In2O3 nanosheets and the CoNi2S4 nanosheets within the composite. The fabricated CoNi2S4-In2O3 composites of nanosheets exhibits the detection of the key intermediate *CH3O during CO2 photoreduction through in situ Fourier transform infrared spectra, while the In2O3 nanosheets and CoNi2S4 nanosheets alone do not show this capability, further verified by the density functional theory calculations. Accordingly, the CoNi2S4-In2O3 composites of nanosheets show the ability to produce CH3OH, whereas the CoNi2S4 and In2O3 nanosheets solely generate carbon monoxide product from CO2 photoreduction.
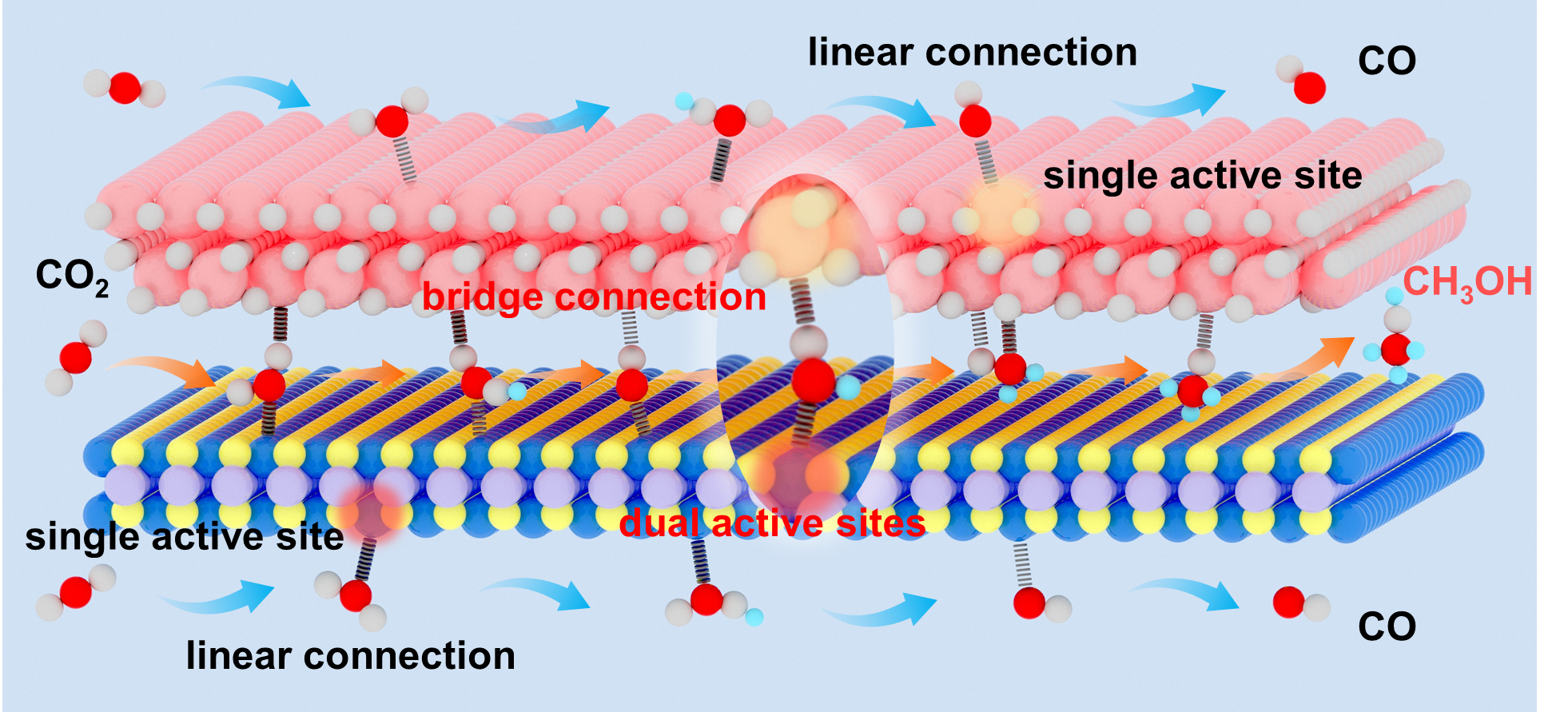
Figure 1. Schematic illustration for CO2 reduction pathways over the composite catalyst with van der Waals contact.